SEO Checklist Validator
Check Your Site's SEO Readiness
This tool validates key SEO elements that developers should implement. Enter values for each item to see if your site meets best practices.
Key Takeaways
- SEO isn’t just marketers’ job - it impacts site performance, code quality, and user experience.
- Understanding keyword research, on‑page basics, and technical health saves redesign cycles.
- Integrating SEO early in the development process reduces later fixes and client churn.
- A small checklist of code‑level SEO tasks can be run on every release.
- Tools like Google Search Console and Lighthouse let developers verify SEO health without leaving the IDE.
What is SEO?
When people talk about SEO is the practice of improving a website’s visibility in search engine results by aligning content, structure, and technical signals with the algorithms that rank pages. In plain terms, SEO helps your site appear when someone types a query into Google, Bing, or any other search engine.
Why SEO matters for developers
A web developer is someone who writes the code, builds the architecture, and ensures a site runs smoothly across devices and browsers. Ignoring SEO can lead to:
- Slow page loads because heavy scripts aren’t optimized.
- Broken crawlability when JavaScript hides important content.
- Missed ranking opportunities because the markup lacks schema or proper headings.
- Extra work later-marketing teams will request “quick fixes” that often mean re‑writing code.
By embedding SEO fundamentals into your workflow, you cut down on back‑and‑forth, keep the site lightweight, and deliver a product that already meets the biggest traffic driver: search.
Core SEO skills every developer should have
Below are the six pillars where a developer’s input directly shapes SEO outcomes.
- Keyword research basics - Knowing the terms users type helps you choose semantic HTML tags, URL structures, and friendly file names.
- On‑page optimization - Proper HTML headings (h1‑h6), meta tags, and alt attributes are pure code; developers own them.
- Technical SEO - Includes crawl budget management, XML sitemaps, robots.txt, and ensuring HTTP status codes are correct.
- Site speed and Core Web Vitals - Page speed, Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) are measured by the browser and affect rankings.
- Structured data - Adding schema markup (JSON‑LD snippets that describe products, articles, FAQs, etc.) lets search engines understand context without extra crawling.
- Mobile‑first responsiveness - A responsive layout is now a ranking factor; breakpoints and viewport meta tags must be set correctly.
How to integrate SEO into the development workflow
Instead of tacking SEO on after the build, weave it into daily tasks.
- Plan with keywords. Before writing code, list primary and secondary keywords. Use them to name components, CSS classes, and image files.
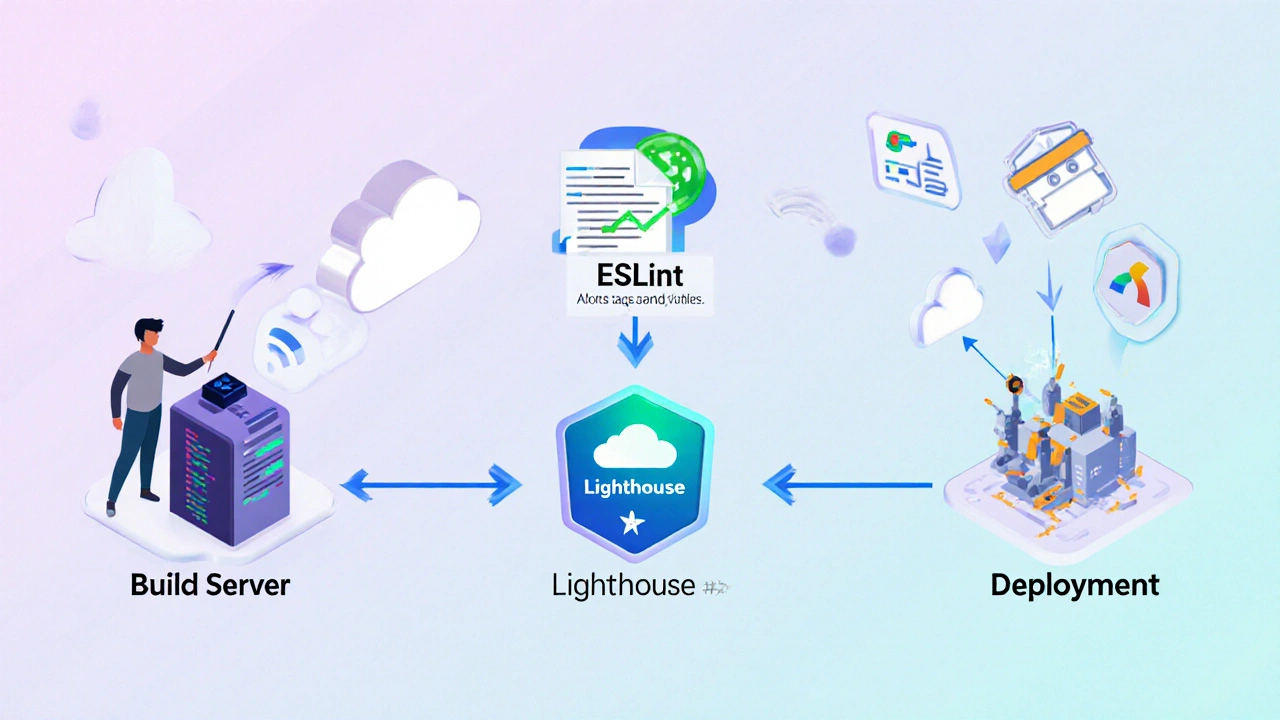
- Set up a lint rule for SEO. Many linters (ESLint, stylelint) can flag missing alt tags or empty title elements. Add the rule to your CI pipeline.
- Run automated audits. Configure Lighthouse to run on every PR. It surfaces performance, accessibility, and SEO warnings early.
- Use headless CMS with built‑in SEO fields. When content editors add a page, the CMS can push meta title, description, and canonical URL directly into the render pipeline.
- Validate with Google Search Console. After deployment, check the Coverage report for crawl errors and the URL Inspection tool for index status.
By treating SEO as a quality gate-just like unit tests-you keep the site search‑ready from day one.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
Even seasoned developers slip up. Here are three frequent mistakes and quick fixes.
- Relying on client‑side rendering for critical content. Search bots may not execute heavy JavaScript. Solution: server‑side render key text or use dynamic rendering (serve a pre‑rendered version to crawlers) for bots.
- Neglecting canonical tags on duplicate pages. Duplicate product listings split link equity. Solution: add a canonical link element pointing to the preferred URL.
- Over‑optimizing anchor text. Stuffing exact‑match keywords can trigger penalties. Solution: keep anchor text natural and vary it across the site.
Quick SEO checklist for developers
| Item | What to verify | Tool/Method |
|---|---|---|
| Title tag | Unique, < 60chars, contains primary keyword | HTML audit, SEO‑linter |
| Meta description | Relevant, < 160chars, adds call‑to‑action | CMS preview, manual check |
| Heading hierarchy | Single H1, logical H2‑H3 flow | Lighthouse SEO audit |
| Image alt attributes | d>Descriptive, include keyword where naturalESLint rule, Chrome DevTools | |
| URL structure | Lowercase, hyphens, no trailing slashes | Manual review, regex test |
| Canonical tag | Present on pages with similar content | View source, Screaming Frog |
| Schema markup | Valid JSON‑LD, matches content type | Rich Results Test |
| Page speed metrics | LCP < 2.5s, CLS < 0.1 | Web Vitals extension, Lighthouse |
Mini FAQ
Do I need a separate SEO specialist if I’m a developer?
You don’t have to replace a specialist, but knowing the basics lets you build SEO‑ready sites and communicate better with the marketing team. For complex campaigns, a dedicated SEO expert still adds strategic value.
Can I automate SEO checks in my CI/CD pipeline?
Yes. Tools like lighthouse-ci, eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y (for accessibility) and custom scripts that run the Google PageSpeed Insights API can fail a build if critical SEO metrics drop below thresholds.
Is schema markup really worth the effort?
When implemented correctly, schema can unlock rich snippets-like star ratings, price ranges, or FAQ drops-leading to higher click‑through rates. The effort is small for static sites and pays off on e‑commerce pages.
How often should I revisit my site’s SEO code?
Treat SEO like any other technical debt. Review major updates (framework upgrades, design overhauls) and perform a full audit at least twice a year, or after any major content shift.
What’s the biggest SEO mistake developers make?
Blocking important resources in robots.txt-a single mis‑configured rule can hide CSS, JS, or images from crawlers, causing ranking drops.





